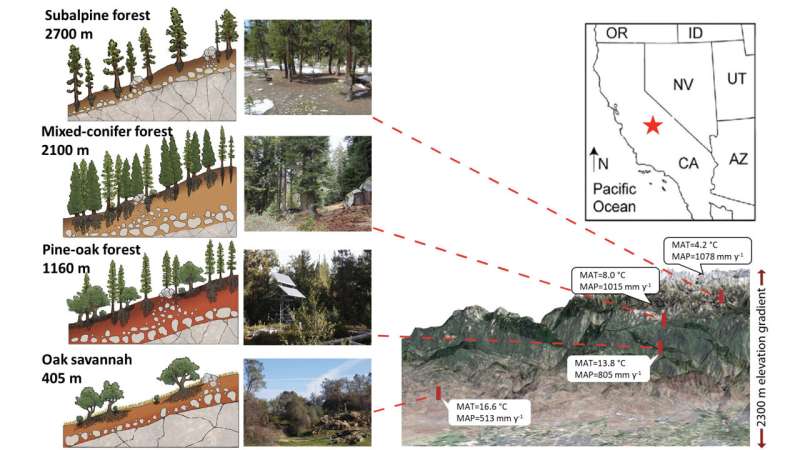
Dust from all around the environment is landing in the Sierra Nevada mountains carrying microbes that are harmful to both vegetation and human beings.
Investigation from UC Riverside displays greater concentrations of the dust are landing at decrease elevations, wherever folks are extra possible to be hiking.
“Pathogenic dust is turning into additional of a threat as the Earth receives drier and much more parched. As it turns out, you can not go climb a mountain to get away from it all,” explained UCR microbial ecologist Mia Maltz, who led the examine.
The researchers element the forms of fungi and bacteria landing from minimal to superior elevations in the mountains in a new Frontiers in Microbiology paper. “Some of these microbes can trigger crop failures and human respiratory sickness,” explained Maltz.
At the reduced elevations, the researchers located more powdery mildews and sooty molds, which can guide to forest blight and crop losses. They also uncovered fungi like Cryptococcus, a sticky yeast, and the plant pathogen Alternaria, the two of which can be inhaled or type bacterial infections in human lungs.
The scientists were being not astonished to understand that dust in the Sierra Nevada was a mixture of soil particles from as much absent as China’s Gobi Desert and as near as California’s San Joaquin Valley. They were surprised, even so, to discover about the combine of microbes in the dust, and wherever they landed in the mountains.
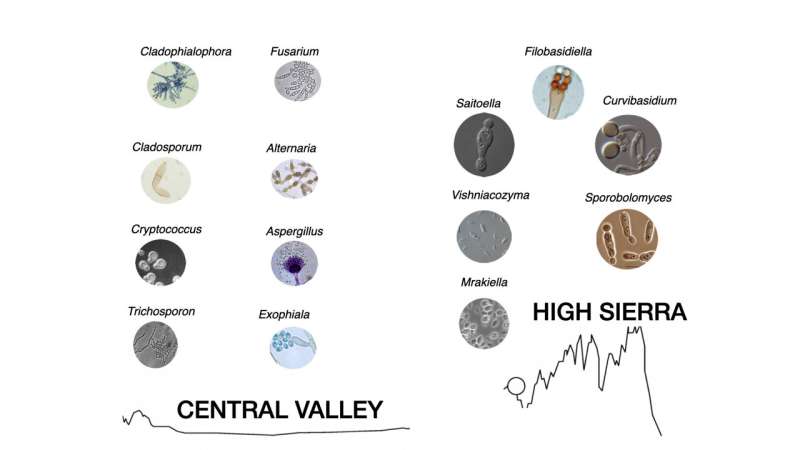
They thought that evenly mixed Asian and regional dust would have the best diversity of germs and fungi on board. As a substitute, they found that when the dust was much more blended, it had reduced species richness.
Dust samples have been gathered at four Critical Zone Observatory network websites in the Sierras, at elevations ranging from 400 to 2,700 meters. The scientists suspect microbes steadily fell out of the dust as they traveled, which could be why fewer types of micro organism and fungi were observed at the major than at the foundation of the mountains.
“I like to think of diversity as becoming a good point, like a safety net. You could drop a few and nonetheless maintain the essential functions of the local community,” Maltz stated. “In this situation, decline of microbial variety at the larger elevations will not appear to be to be a adverse we are getting rid of pathogens rather.”
Some dust traveling the globe and landing in the Sierra Nevada is natural, and even advantageous for mountain ecosystems. Dust carries fungi and bacteria that aid decompose natural and organic particles and enrich the soil.

There are also practical microbes in the dust that empower vegetation to take up nutrients like phosphorus that are desired for development. Pine trees, in this ecosystem, derive far more than 80% of what they have to have to generate their needles from dust.
“Without the need of dust, trees wouldn’t have what they need to flourish and fix carbon from the atmosphere at the amount they’re at this time executing it,” reported UCR environmental microbiologist and analyze co-author Emma Aronson.
However, in a long run local climate, there are possible to be a lot more droughts, ensuing in more dust. If a better proportion of the microbes landing in the Sierra Nevada are pathogenic, that could have an affect on which species of vegetation and animals are able to persist.
“With enhanced die-off of massive conifers and other plants, there would be considerably less carbon sequestered than there has been traditionally, and the environment could get even hotter,” Aronson reported.

Nevertheless the researchers did not established out to study climate change, the study gives a glimpse of what could come about when there is less snowpack and for a longer time dry seasons.
“Mountains are a superior organic laboratory for local climate transform because it is really cooler and wetter at the leading, and hotter and drier at the foundation. They give us predictive ability about how ecosystems will adapt to the adjustments we’re previously observing,” Maltz stated.
Modeling suggests decline of biocrusts by 2070 could end result in maximize of 15% more dust emissions
Mia R. Maltz et al, Landscape Topography and Regional Drought Alters Dust Microbiomes in the Sierra Nevada of California, Frontiers in Microbiology (2022). DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.856454
University of California – Riverside
Quotation:
Drought improves microbe-laden dust landing in Sierras (2022, August 9)
retrieved 9 August 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-08-drought-microbe-laden-sierras.html
This doc is subject to copyright. Aside from any fair dealing for the goal of private research or investigation, no
part may perhaps be reproduced without the prepared authorization. The information is provided for information and facts uses only.




