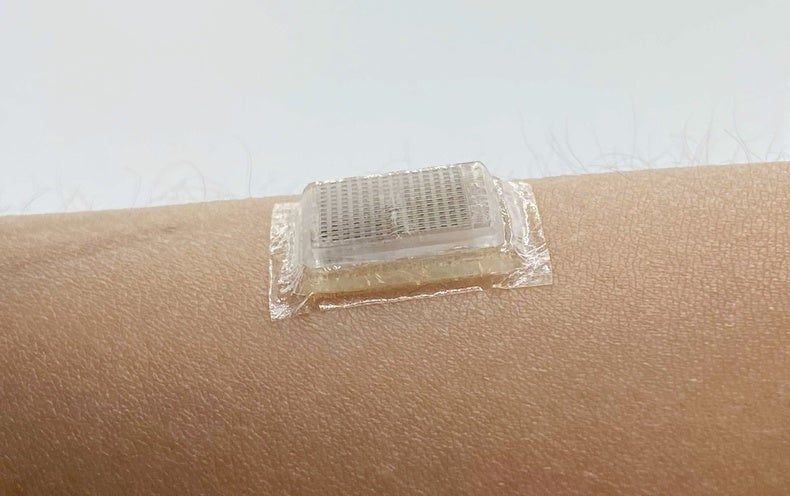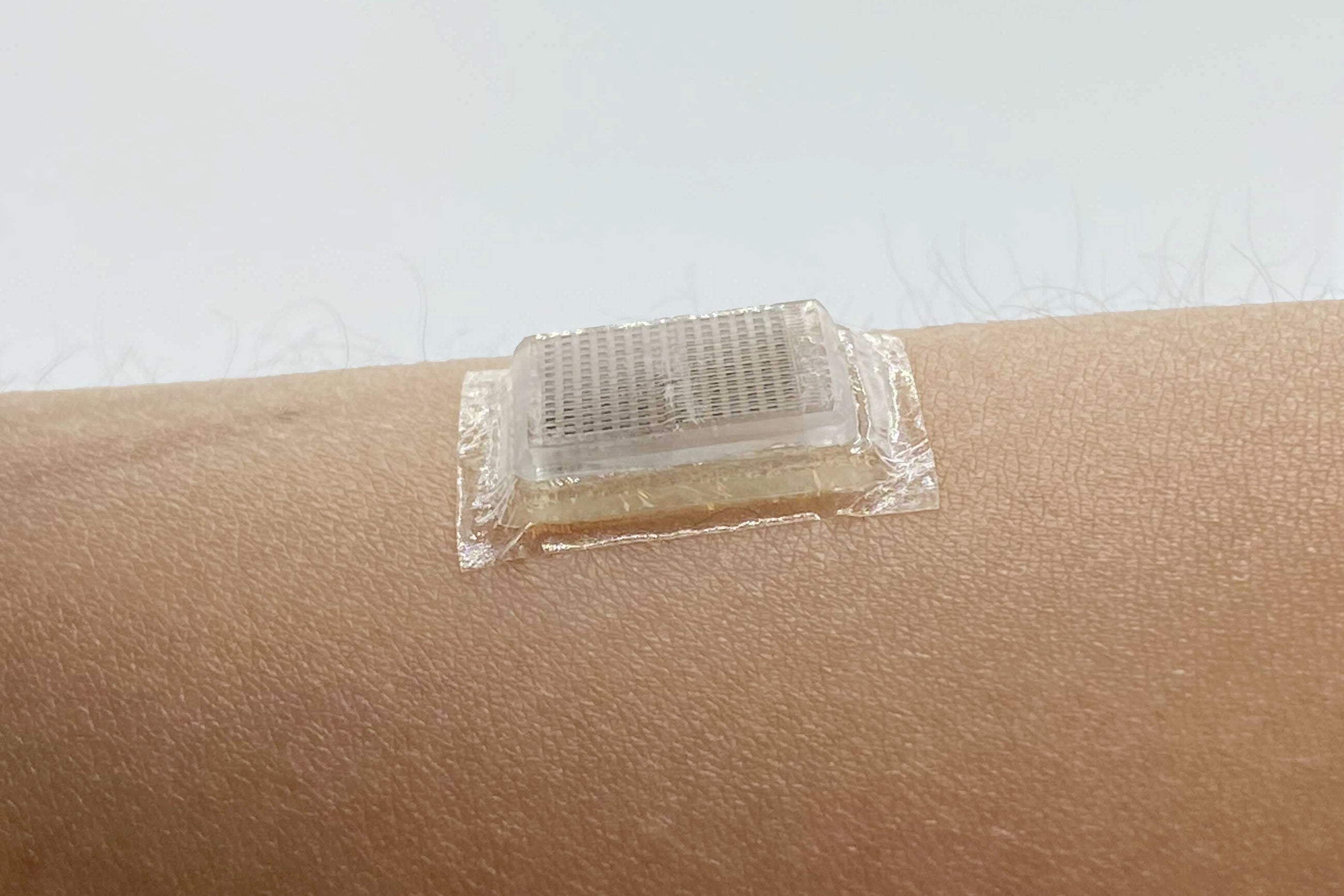
Ultrasound scanners, which impression the inside of the human entire body, are a existence-saving healthcare device. Now researchers have shrunk the handheld ultrasound probe—which normally involves a remarkably properly trained technician to shift about the skin—down to a flat chip that is the sizing of a postage stamp and sticks to the skin with a particular bioadhesive. The new unit can file superior-resolution videos for two times at a stretch, capturing blood vessels and hearts laboring throughout work out or stomachs expanding and shrinking as examination subjects gulp juice and then digest it.
“The elegance of this is, abruptly, you can adhere this ultrasound probe, this slim ultrasound speaker, to the overall body in excess of 48 several hours,” states Xuanhe Zhao, a mechanical engineer at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and co-writer of a paper describing the new product, which was printed in Science on Thursday. By recording nevertheless photos and movies of interior organs in the course of this time, a wearable imaging machine could be utilised to diagnose heart assaults and malignant tumors, test the effectiveness of prescription drugs and assess common heart, lung or muscle health. “This can potentially modify the paradigm of medical imaging by empowering long-phrase continual imaging,” Zhao provides, “and it can alter the paradigm of the discipline of wearable gadgets.”
Standard ultrasounds are excellent at peering beneath the pores and skin with out producing destruction to the entire body, but obtain to this kind of scans is minimal. “The typical handheld ultrasound calls for nicely-trained professionals to place the probe properly on the pores and skin and utilize some liquid gel in between the probe and skin,” suggests Nanshu Lu, a mechanical engineer at the College of Texas at Austin, who was not involved in the new investigation but co-wrote an accompanying examination in Science. “And as you can consider, it’s very monotonous and very brief-term, really constrained.” Simply because they call for an professional human operator, Lu clarifies, these scans are high priced, and they cannot be employed in tests exactly where the topic is working out or placing their overall body beneath tension from heat or extreme environments. “Conventional ultrasounds have a lot of restrictions,” she suggests. “If we can make ultrasound sensors wearable and cell and obtainable, it will open up a good deal of new choices.”
Many thanks to their likely flexibility, other researchers have tried to make stick-on ultrasound patches. But in order to adhere to tender, stretchy pores and skin, earlier devices were built to be stretchable on their own. This type variable weakened impression excellent simply because it could not accommodate as numerous transducers—units that, in this circumstance, remodel electrical electricity into audio waves with frequencies way too superior for human ears to detect. An ultrasound probe sends these waves as a result of a layer of gooey gel into the human overall body, where they bounce off organs and other inside structures and then return to the transducer array. This converts the mechanical waves again to electrical indicators and sends them to a laptop for translation into illustrations or photos.
The more transducers, the greater the picture good quality. “It’s really very similar to a digital camera,” explains Philip Tan, an electrical engineer and a graduate scholar at Lu’s lab at U.T. Austin, who was also not involved with the new examine but co-wrote the examination piece. A stretchy adhere-on ultrasound probe, which have to be capable to flex every time the skin moves, simply cannot pack as several transducers into the array—and when the wearer moves, the configuration of transducers shifts and makes it challenging to capture secure pictures.
In its place of generating the product itself stretchy, Zhao and his group attached a rigid probe, just a few millimeters thick, to a versatile layer of adhesive. This adhesive replaces the gooey liquid put between a standard ultrasound wand and the pores and skin, and it is a hybrid of a water-rich polymer named a hydrogel and a rubberlike materials identified as an elastomer. “It is a piece of good hydrogel made up of around 90 % h2o, but it is in a sound state like Jell-O,” Zhao says. “We address the surface of this Jell-O with this extremely skinny membrane of elastomer so that the h2o inside of the Jell-O will not evaporate out.” This bioadhesive not only caught the probe firmly to the skin for 48 several hours, but it also delivered a cushioning layer that guarded the rigid electronics from the flexing of skin and muscular tissues.
To picture diverse body units, Zhao’s workforce examined variations of the probe that make waves at unique frequencies and therefore penetrate the human body to various depths. For occasion, a higher frequency such as 10 megahertz could make it to a few of centimeters beneath the pores and skin. The researchers made use of this frequency to capture the action of blood vessels and muscle mass as exam subjects shifted from sitting to standing or exercised vigorously. A lower frequency of 3 megahertz goes deeper, additional like 6 centimeters, to seize inner organs. Making use of this frequency, the researchers imaged the 4 chambers of a subject’s coronary heart, and recorded the stomach of a different emptying out as their process processed a couple of cups of juice. The scientists also when compared the photographs gathered with their rigid ultrasound probe with those captured by a stretchable ultrasound device, Zhao says. “You can see the resolution of ours is virtually a person order of magnitude [10 times] bigger than the stretchable ultrasound,” he provides.
An imaging gadget that maintains a continual view around certain pieces of the human body could be utilized to observe and diagnose a assortment of ailments. Medical professionals could preserve a shut eye on the progress of a tumor about time. Anyone at high risk of hypertension could possibly wear an ultrasound patch to measure their high blood tension, alerting them when the strain spikes or monitoring no matter if a medicine is encouraging. A COVID individual could continue to be household, understanding that an imaging unit would warn them if their illness triggered a lung an infection extreme ample to need hospitalization. Probably the most significant application could be in the detection and diagnosis of coronary heart assaults. “Cardiovascular illness is … the main induce of death in the entire globe, also in the U.S.,” Zhao suggests. Coronary heart health and fitness is on the radar of other wearable machine developers. For instance, intelligent watches these kinds of as the Apple Enjoy are able of monitoring the electrical signals that point out coronary heart action with a so-called electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This can be utilized to diagnose heart attacks—at the very least in some situations. “There are already studies showing that EKG can only diagnose close to 20 percent of coronary heart attacks. The greater part of coronary heart assaults actually involve imaging modalities, these kinds of as ultrasound imaging, to diagnose,” Zhao says. Steady imaging of a patient’s heart could capture their indicators and provide an early analysis.
“The major offering position of this new device is that it opens new varieties of health-related prognosis that just cannot be accomplished in a static setting,” Tan says. To evaluate heart overall health, for instance, it is useful to measure the organ’s exercise although exercising—but it’s tough to hold an ultrasound wand from a running subject’s goo-lined chest. “With a wearable ultrasound patch, where you would not have to hold the transducer on the human being, they were really ready to display that you are equipped to get very substantial-good quality images of the heart even in the course of motion,” Tan provides.
The bioadhesive unit is not ready for action yet, having said that. For one issue, it however has to be physically plugged into a laptop that can accumulate and examine the details the probe produces. “We join this probe via a wire to a information acquisition program,” Zhao says. “But my group is doing work extremely tricky to miniaturize and combine anything into our wireless machine.” He finally plans to improve the patch with a miniaturized electrical power source and a wireless info-transmission method. This is a feasible objective, Lu and Tan concur, many thanks to shrinking electronic factors and fabrication approaches that make it possible for these capabilities to be blended into an “ultrasound on a chip.” Lu suggests that if the area can bring in federal and personal investments, these a gadget could be possible in just five decades, even though it would nonetheless have to earn acceptance from federal regulators.
In the end, ultrasound stickers could join the ranks of wearables that observe human overall health, which include current units that obtain facts about coronary heart rate, sleep high quality and even worry. “Our human system is radiating a whole lot of a highly individual, highly continuous, distributed and multimodal details about our well being, our emotion, our awareness, our readiness, and so on. So we’re whole of information,” Lu says. “The issue is how to get them reliably and constantly.”